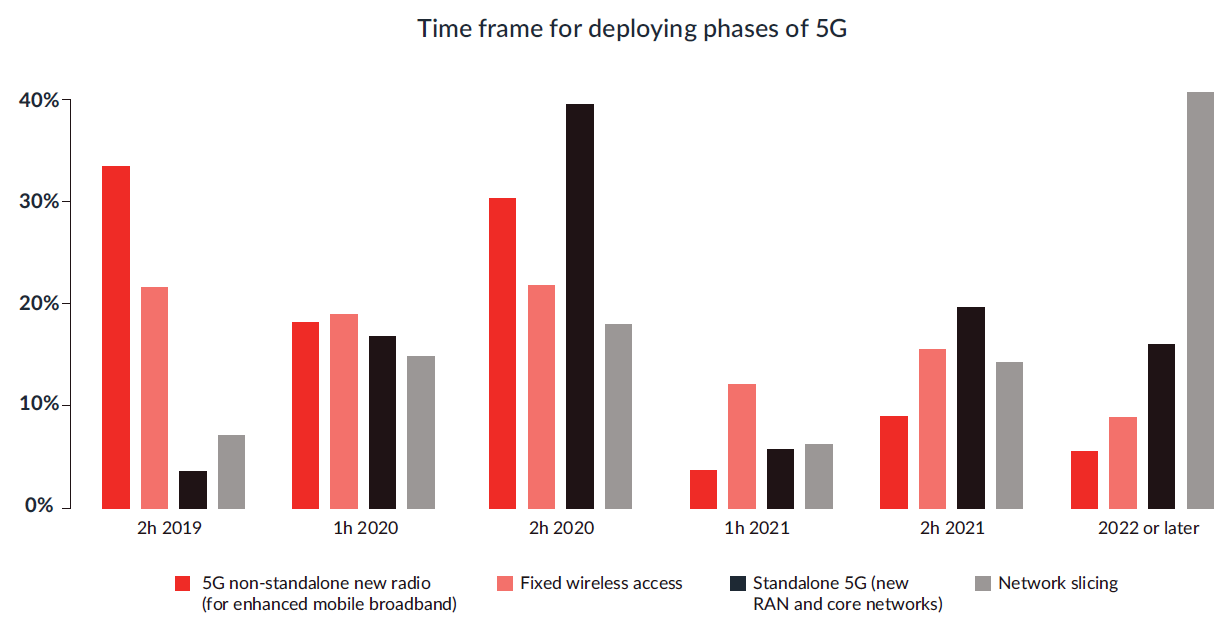
TMF 提供了四个选项:5G NSA, FWA, 5G SA, 网络切片;针对运营商的倾向性调查(调研时间 2019)。
网络切片部署时间靠后是普遍观点,我也认为 2022 年前不可能规模部署;而且所谓的规模部署到什么样的程度?还需要进一步的验证。
TMF 也给出了理由:
Slicing sticks out in the chart. Often described as one of the most important characteristics of 5G because it will help CSPs achieve the long-sought ability to differentiate and monetize services based on quality, large-scale network slicing implementations aren’t expected until 2022 or later. This conservative projection is due in part to the need for slices to operate end to end in the prescribed manner, which requires standalone 5G.
Standalone 5G is the grand prize of the next-generation network, and its capabilities are what really matter to enterprises. With new core and radio access networks, be they centralized or virtual RANs, Standalone 5G will support and drive the triumvirate of differentiating capabilities – co-creation, network slicing and edge computing.
However, the big push for Standalone 5G is not expected until the latter half of 2020 after standards are in place.
从组网建设角度,5G 分为 5G NSA 和 5G SA 两种。
5G NSA(Non-Stand Alone, 非独立组网),指的是利用现有 4G 基础设施对 5G 网络进行部署。基于 NSA 架构的 5G 承载仅承载用户数据,控制信令仍然通过 4G 网络传输。
5G SA (Stand Alone,独立组网)指新建 5G 网络,包括基站、回程链路和核心网。换句话说,SA就是从零开始建设5G网络。
2019 年各地商用的 5G 基本都是 NSA 版本,后面逐步向 5G SA 演进。围绕 5G SA 的收益倾向,附图是 GSMA 针对全球运营商读者的调研。
从反馈得分高低看,分别为:
(1) 支持 mMTC(大规模机器通信);
(2) 简化网络结构;
(3) 优化网络成本;
(4) 支持...
凯捷咨询 Capgemini 针对全球 1,000 名企业管理者(总监及以上)进行调研,了解对 5G 部署模式的企业选择倾向性。
凯捷归纳了四种典型模式:
(1) 企业使用私有频率,部署 5G 专网;
(2) 混合模式,同时使用 5G 公网和 5G 专网;
(3) 使用虚拟专网(比如:5G 切片);
(4) 基于 5G 公网。
从调研反馈看,模式一(5G 专网 + 私有频率)是倾向性最强的选项;其次是模式三(5G 切片)。
Dell’Oro 研究显示,2023 年中国运营商供采购了 2300 万套 FTTR ONT(光猫)设备,其中主光猫和从光猫的比例大约是 1:1.01。
截止到 2023 年底,中国运营商拥有 FTTR 订阅用户约 3,500 万户,预计到 2024 年可提升到 4,800 ~ 5,300 万户。到 2026 年有望达到 8,000 万户。


